Abstract
Background: Endothelial dysfunction underlies the two main complications of chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy, i.e. cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). The purpose of this retrospective analysis was to evaluate and validate the Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX)) as predictor for CRS and ICANS in patients receiving CD19-directed CAR-T cells.
Methods: In this retrospective study, the training cohort recruited 107 patients treated with CAR-T cells at the University Hospital Heidelberg (n=83) and Charité University Medicine Berlin (n=24) from Oct 1, 2018, to March 31, 2021. Patients from the validation cohort (n=93) received CAR-T cells within the ZUMA-1 trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT02348216).
The training cohort included 37 and 34 patients with relapsed / refractory (r/r) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) treated with Axi-cel and Tisa-cel, respectively, 1 patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treated with Tisa-cel, 2 patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) treated with KTE-X19 on an early access program; and 5 patients with LBCL, 5 patients with MCL, 5 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, 4 patients with follicular lymphoma, and 14 patients with ALL treated with the 3 rd generation CAR-T HD-CAR-1. Median age was 57 (20-81) years, 72% were male. The 93 patients of the validation cohort all had r/r LBCL and received Axi-Cel.
EASIX and serum levels of endothelial stress markers (angiopoietin-2, suppressor of tumorigenicity-2, soluble thrombomodulin and interleukin-8) were measured before start of lymphodepletion (EASIX-pre), and on days 0, 3, and 7 after CAR-T infusion. Primary endpoints were severe CRS and/or ICANS (grades 3-4).
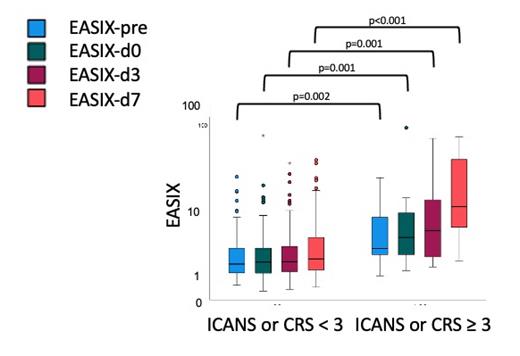
Results: Of the 107 patients of the training cohort, 61 patients (58%) developed CRS grades 1-4 and 24 patients (22%) developed ICANS grades 1-4. Higher grade CRS (grade ≥ 3) was seen in 6 patients (6%) with a median onset of 4 (0-14) days, while grade ≥ 3 ICANS occurred in 11 patients (11%; median onset 8 (4-17) days). EASIX values increased continuously from lymphodepletion to day 7 after CAR-T cell application (EASIX-pre 2.0 (0.5-76.6, interquartile range (IQR) 1.2/4.1); EASIX-d0 2.0 (0.3-91.5, IQR 1.2/4.2); EASIX-d3 2.4 (0.3-69.1, IQR 1.3/4.9) and EASIX-d7 2.7 (0.4-94.0, IQR 1.4/7.5)).
In the validation cohort, Grade ≥ 3 CRS was observed in 10 patients (11%) and grade ≥ 3 ICANS in 28 patients (30%). Similar to the training cohort, EASIX values rose from lymphodepletion to day 3 after CAR-T cell application (EASIX-pre 1.8 (0.3-106.1, IQR 1.0/4.7); EASIX-d0 2.0 (0.3-120.4, IQR 1.1/4.1) and EASIX-d3 2.7 (0.3-57.9, IQR 1.7/6.2).
In both cohorts, all EASIX values (pre, d0, d3, d7) were significantly higher in patients who developed either grade 3-4 CRS, ICANS or both (see Figure 1 for the training cohort).
EASIX predicted grade 3-4 CRS and ICANS before lymphodepleting therapy (-pre), on day 0 and on day 3 in both cohorts: AUC EASIX-pre, training cohort 0.73 (0.62-0.85, p=0.002), validation cohort 0.76 (0.66-0.87, p<0.001). An optimized cut-off for EASIX-pre (1.86) identified in the training cohort associated with an odds ratio (OR) of 5.07 (1.82-14.10), p=0.002 in the validation cohort in multivariable binary logistic regression analysis including age, gender, diagnosis and disease stage.
Serum endothelial stress markers did not predict the two complications when assessed before CAR-T infusion, but diagnostic markers were strongly associated with CRS and ICANS grade 3-4 on day+7.
Conclusions: EASIX-pre is a validated predictor of severe complications after CAR-T therapy and may help to tailor safety monitoring measures according to the individual patient's needs.
Data on patients from the ZUMA-1 trial were provided by Kite/Gilead.
Penack: Astellas: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Neovii: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Therakos: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Priothera: Consultancy; Shionogi: Consultancy; Omeros: Consultancy. Schmitt: MSD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Apogenix: Research Funding; Hexal: Other: Travel grants, Research Funding; TolerogenixX: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Kite Gilead: Other: Travel grants; Bluebird Bio: Other: Travel grants; Novartis: Other: Travel grants, Research Funding. Müller-Tidow: Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Bioline: Research Funding. Bullinger: Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Menarini: Consultancy; Sanofi: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bayer: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy; Hexal: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Dreger: Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Riemser: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal